Table of Contents
Location: no longer available
username: immuser
password: !immuser
System overview
Brainstorm is a linux PC workstation featuring:
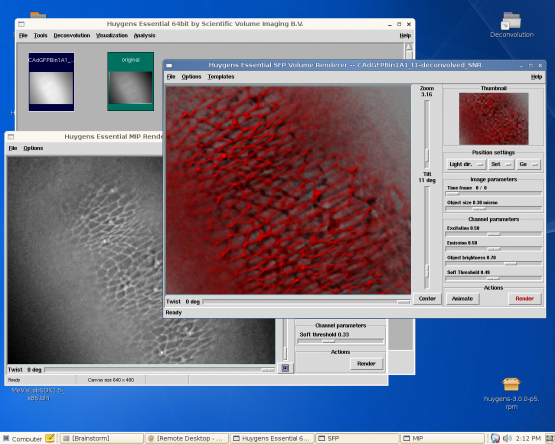
- Huygens Essentials and Huygens Script prepared for Widefield and Confocal deconvolution (blind and non-blind).
- A dual core 64-bit processor at 2.13GHz
- 4GB RAM memory
- Suse 64-bit linux
The system has been configured to be straightforward and easy to use.
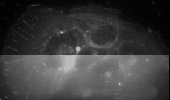
- mCherry labeled actin in an Hepatocites (upper part deconvolved, lower part raw data). XYZ 3D reconstruction , Specimen: Carina Santos (2007), Instituto de Medicina Molecular, Lisboa, Portugal.
What is Deconvolution?
Deconvolution in Optical Microscopy
“Deconvolution is often suggested as a good alternative to the confocal microscope. Deconvolution is a computationally intensive image processing technique that is being increasingly utilized for improving the contrast and resolution of digital images captured in the microscope. The foundations are based upon a suite of methods that are designed to remove or reverse the blurring present in microscope images induced by the limited aperture of the objective. Nearly any image acquired on a digital fluorescence microscope can be deconvolved.”
Microscopes used with Deconvolution
Almost any fluorescence microscope can be used with Deconvolution. For example:
How to access Brainstorm
There are two ways to access the Brainstorm server in order to use the deconvolution software:
- Through the Huygens Remote Manager - the easiest way to do deconvolution, no need to book the system.
- By Remote Desktop using VNC.
Huygens Remote Manager
The Huygens Remote Manager is quite simple to use and is quite 'nice' if multiple people are using the system. The idea is that you can add the images you want to deconvolve into a queue and after a few hours they will be deconvolved and ready to download.
To Deconvolve
Note: will only work inside IMM.
- Go to http://brainstorm/hrm and create a user if you don't already have one.
- Next go to \\brainstorm\deconvolution\HRM\<your username here>\huygens_src and put the data files you want to deconvolve there.
- Now in http://brainstorm/hrm after you create your settings you should be able to see your files ready to deconvolve.
Remote Desktop using VNC
VNC is less friendly but lets you deal with the Huygens software directly. You can access the VNC interface through an internet browser like Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox. Use the address: http://brainstorm:5801 - will only work inside IMM. Here's a small tutorial.
- You can also use a vnc client like tightvnc.
Note: If you're going to use VNC, do not forget to book the system in the booking system before using it. There can only be one user using the system at a time!
Moving files From and To the Brainstorm server
The folder Deconvolution (visible in the Brainstorm Desktop) is shared in the network (no password or username) in order for you to transfer you files:
- On windows: go to the start menu and select run, next enter the text "\\brainstorm\deconvolution" and press Enter.
- On apple mac: in finder go to the menu option go and connect to server, write "smb://brainstorm/deconvolution".
Note: For deconvolution with the Huygens Remote Manager use the folder
brainstorm\deconvolution\HRM\<your_Huygens_Remote_Manager_username>\huygens_src.
Deconvolution Tips and Tricks
Very important: your data must have almost no saturation!
When you do deconvolution there's some information that you need to know:
| Microscope | Objective | NA | Type | Pixel Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeiss Axiovert 200M | 10x | 0.3 | Dry | 983 nm (bin 1) |
| Zeiss Axiovert 200M | 20x | 0.5 | Dry | 491 nm (bin 1) |
| Zeiss Axiovert 200M | 40x | 0.75 | Dry | 246 nm (bin 1) |
| Zeiss Axiovert 200M | 63x | 1.4 | Oil | 156 nm (bin 1) |
| Zeiss Axiovert 200M | 100x | 1.4 | Oil | 98 nm (bin 1) |
| Zeiss LSM 710 | 10x | 0.3 | Dry | See info below |
| Zeiss LSM 710 | 20x | 0.5 | Dry | See info below |
| Zeiss LSM 710 | 40x | 1.3 | Oil | See info below |
| Zeiss LSM 710 | 63x | 1.4 | Oil | See info below |
| Medium | Refraction Index |
|---|---|
| Air | 1.00 |
| Water | 1.33 |
| Glycerol + Water | 1.4 |
| Halocarbon 400 | 1.412 |
| Halocarbon 700 | 1.414 |
| Glycerol | 1.456 |
| Liquid Vectashield | 1.47 |
| Paraffin oil | 1.482 |
| m-xylene | 1.497 |
| Immersion Oil | 1.515 |
| Glass | 1.52 |
| Monobromonaphthalene | 1.655 |
| Methyl Iodide | 1.76 |
Pixel (Pinhole) size for Zeiss confocal microscopes
- To get the pinhole size of the Zeiss LSM 710 open your image in ZEN
- Press the
Infobutton in the Image Window and a panel should appear, in that panel you have written the pinhole size for each channel. - Next go to this link to get the pinhole size you should use with Huygens.
External links
- Huygens Remote Manager: a Web Interface for High-Volume Batch Deconvolution. Imaging & Microscopy (2007) V 9, No. 2, pp 57-58.
- SVI Huygen Essentials wiki - tutorials and information